Purpose of the flight and payload description
The mission was primarly intended to perform a technological test flight of several CNES balloon subsystems. Aditionally it carried a small payload called COCOTE (COmpact COmpton TElescope) that involved testing an innovative silicon-based detector in extreme conditions. Conducted by a Franco-German collaboration, between the Institut de Recherche sur les lois Fondamentales de l'Univers (IRFU-CEA) and the Tübingen University, the project is aimed to advance neutrino physics and gamma-ray astronomy, addressing dark matter and cosmic photon detection. The system, developed in just three months, served as a precursor to future space missions like eASTROGAM and helped refine detector technologies for astrophysical and particle physics applications
The instrument onboard the COCOTE mission was composed of silicon pixel detectors designed for Compton scattering detection and innovative photodetection technologies to track gamma-ray interactions. This configuration enabled precise measurements of high-energy photons in a compact form factor, suitable for balloon or space applications. Besides the acronym of the detector, the system was located inside a pressure cooker which in French is called a COCOTTE.
Details of the balloon flight
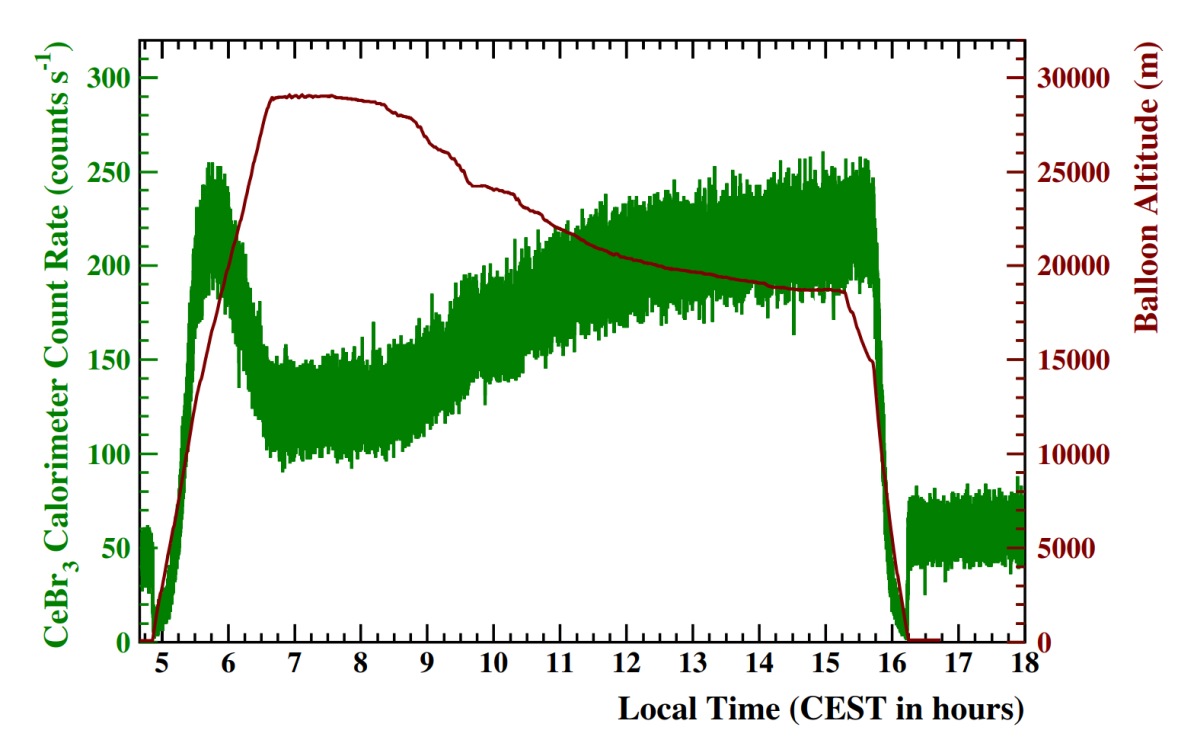
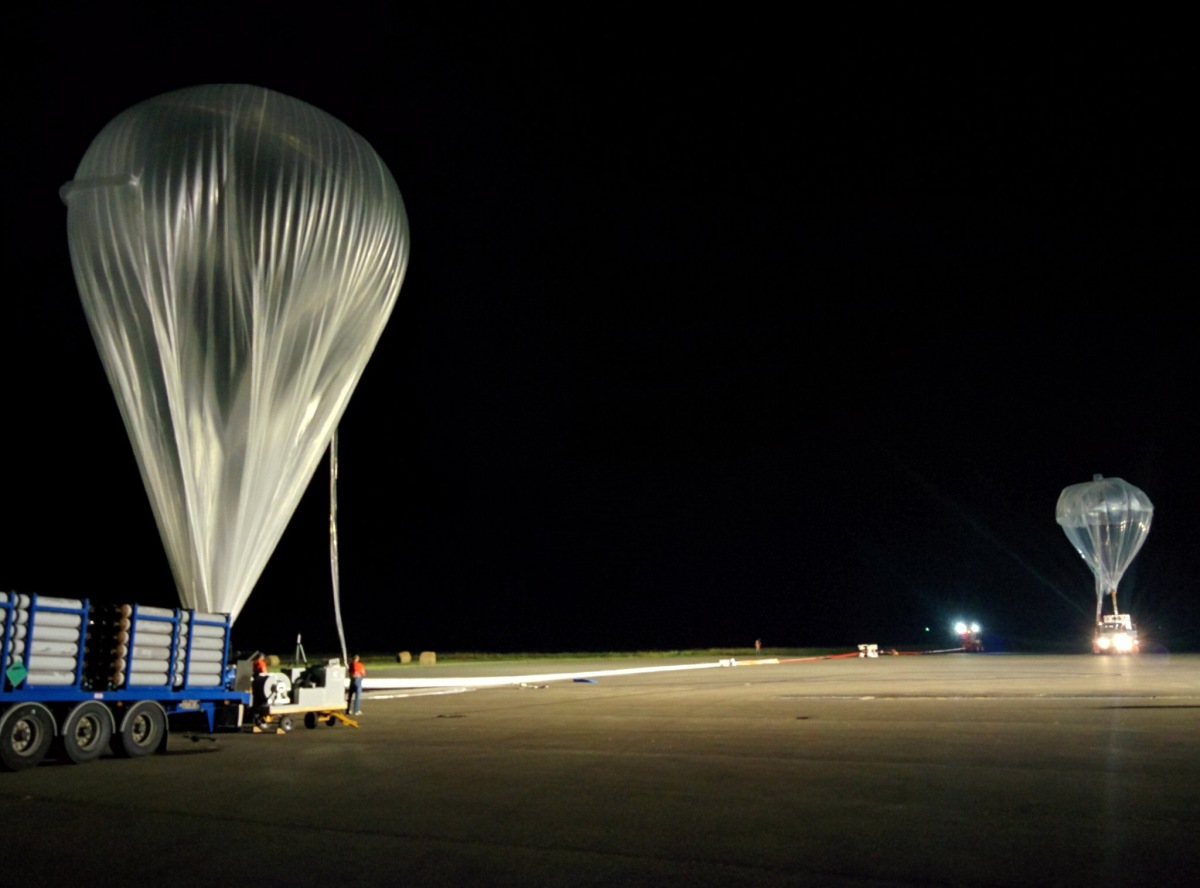
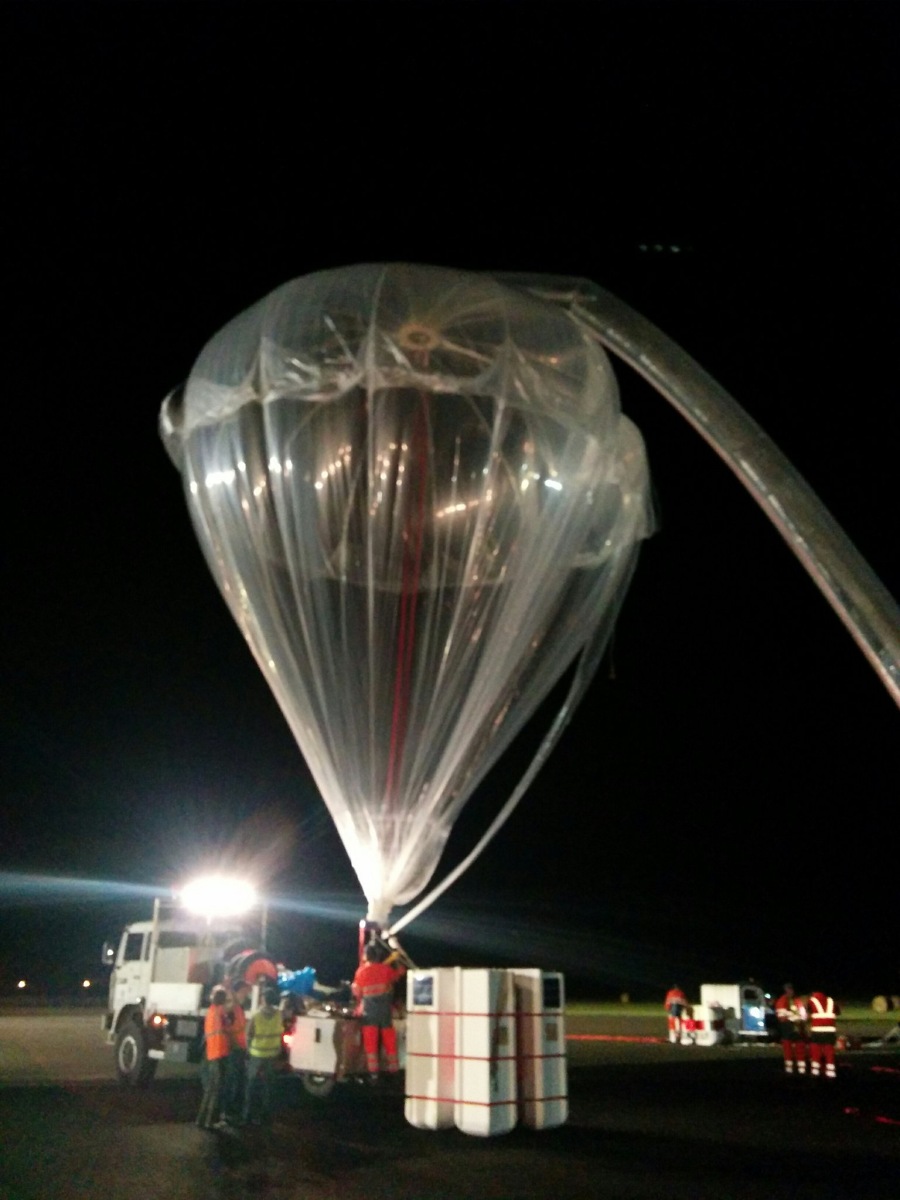
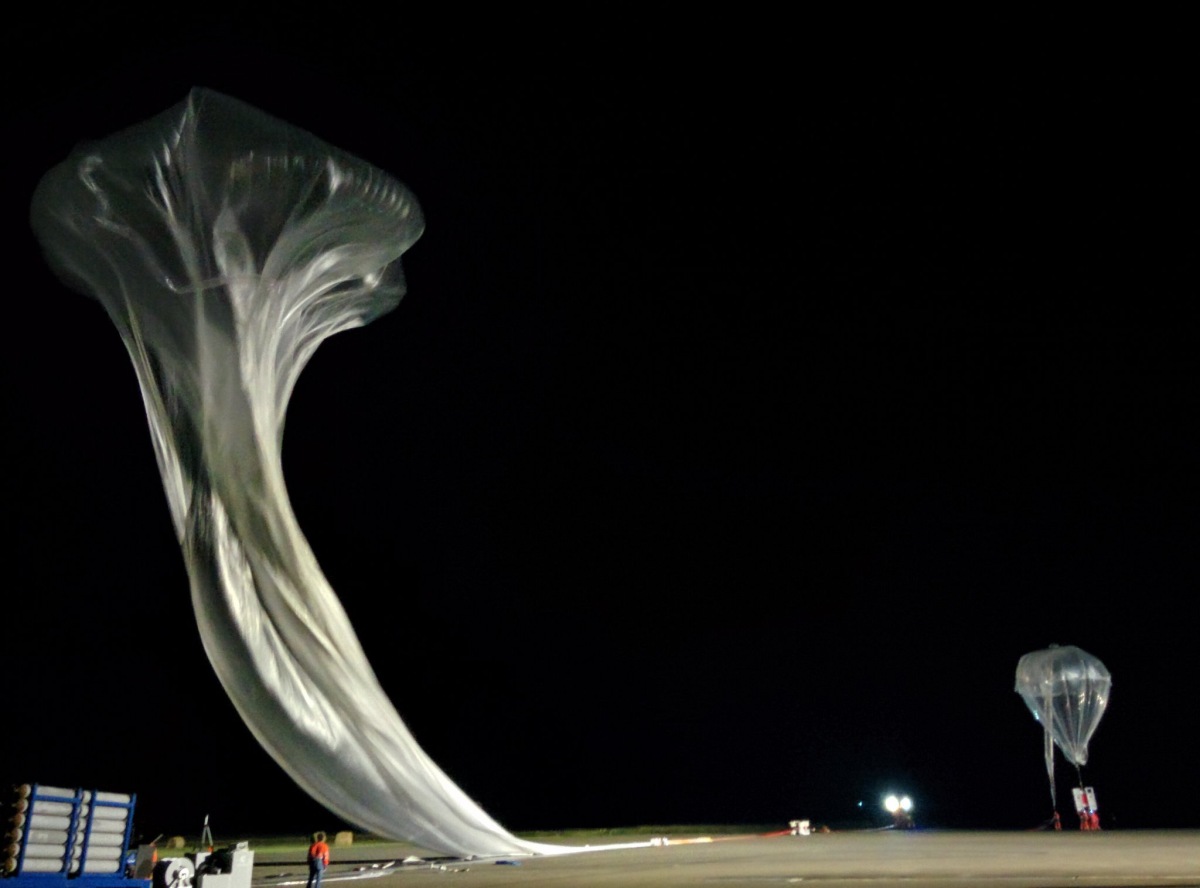
Balloon launched on: 7/2/2016 at 4:50 cest
Launch site: Centre de Lancement de Ballons CLBA, Aire Sur L'Adour, Landes, France
Balloon launched by: Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 7/2/2016 at 16:15 cest
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 11 h 25 m
External references
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.






