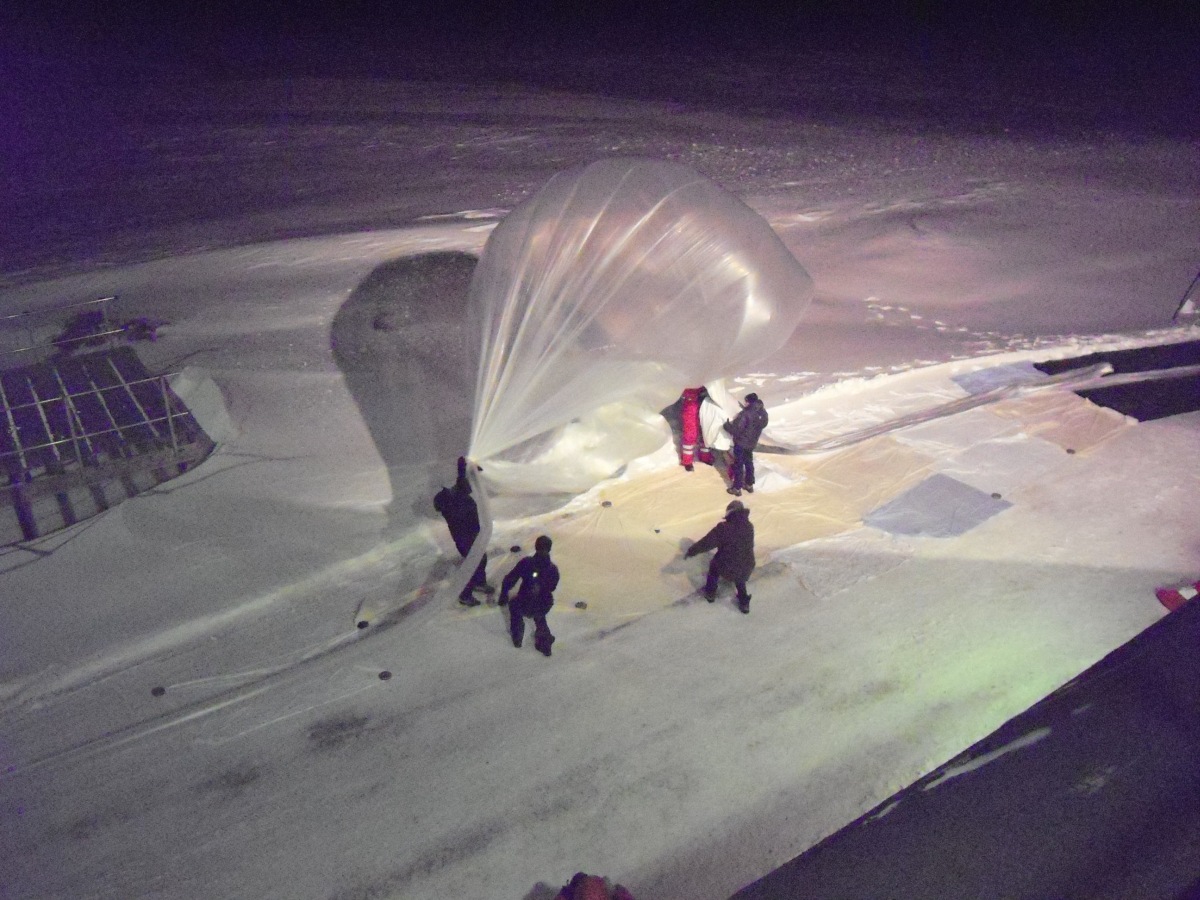
Purpose of the flight and payload description
The aim of the POP (Polar Observation Platform) initiative was to demonstrate the feasibility of long-duration stratospheric-balloon flights during the polar night in the Arctic. The effort was carried out through a cooperation between the University la Sapienza of Rome and the ISTAR-Group (International Science Technology and Research) from the United States. Balloons were launched with the support of the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche that offered the facilities of the Dirigible Italia base in Ny Alesund, Spitzbergen Island in Svalbard.
Objectives of the 2011 campaign was to observe, in real time, the polar winter night sky stratospheric wind trajectories for planning future campaigns with heavy lift Long Duration Balloons (LDB) during the polar night. The advantage of a winter flight offers the science teams observations without the solar radiation experienced during the summer months.
The payload carried out by the balloon was simple battery powered ARGOS / GPS transmitter that delivered time, temperature, speed, heading, and altitude.
Details of the balloon flight
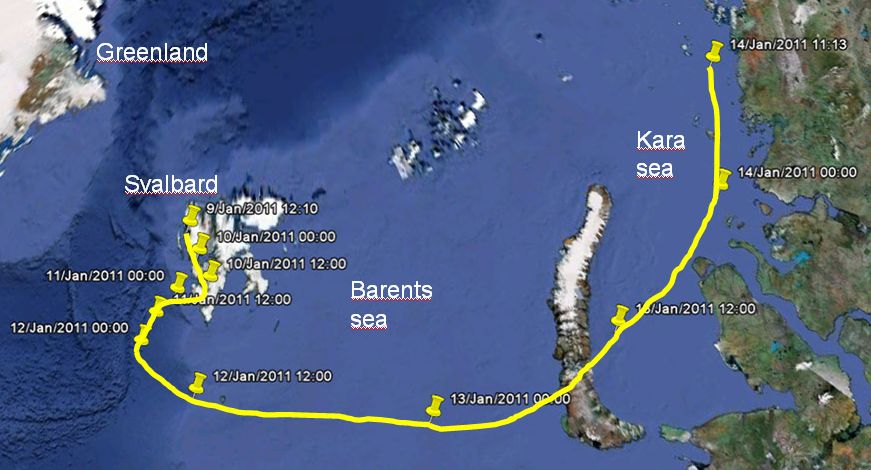
Balloon launched on: 1/9/2011 at 12:30 utc
Launch site: Ny-Alesund, Svalbard, Norway
Balloon launched by: ISTAR (International Science Technology And Research)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon Near Space Corporation - 2523 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 1/14/2011 at 11:00 utc
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 5 d 12 h
Landing site: In the Kara Sea, offshore Tamir peninsula, Russian Federation
The balloon was launched from Ny Alesund, Spitzbergen Island on January 9, 2011 at 12:30 utc in mild conditions with a temperature of -8º C and wind of 1 kts until inflation began when the winds rose to 12 kts throughout the inflation and launch. Ironically, after the balloon was released from the spool the winds calmed down again and remained calm for the next 24 hours. The balloon maintained a nominal ascent and remained at the prescribed float altitude for 5.5 days. The trajectory shown in the map above confirms that the stratospheric winds during the winter months can support a Long Duration Balloon (LDB) flight.
External references
- Polar winter balloon launches in Svalbard Stratocat website
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.


