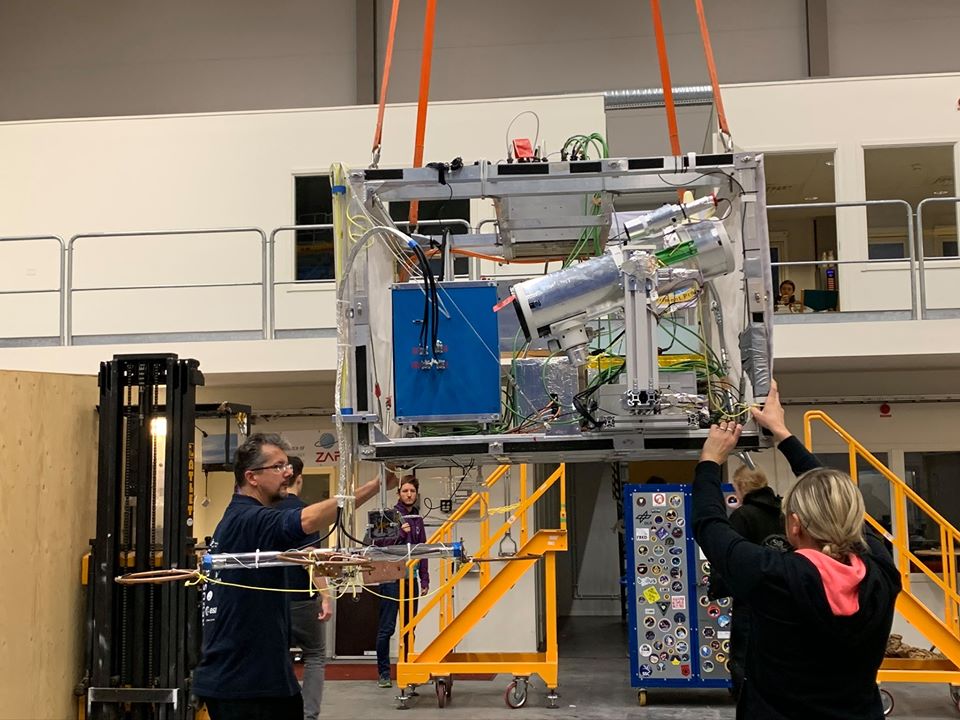
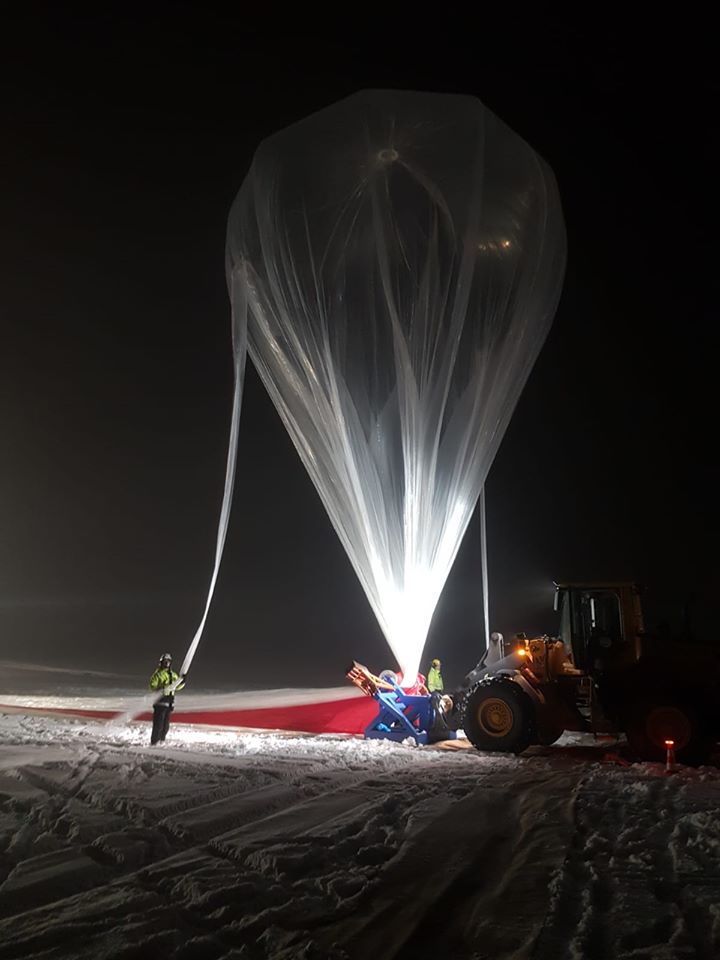
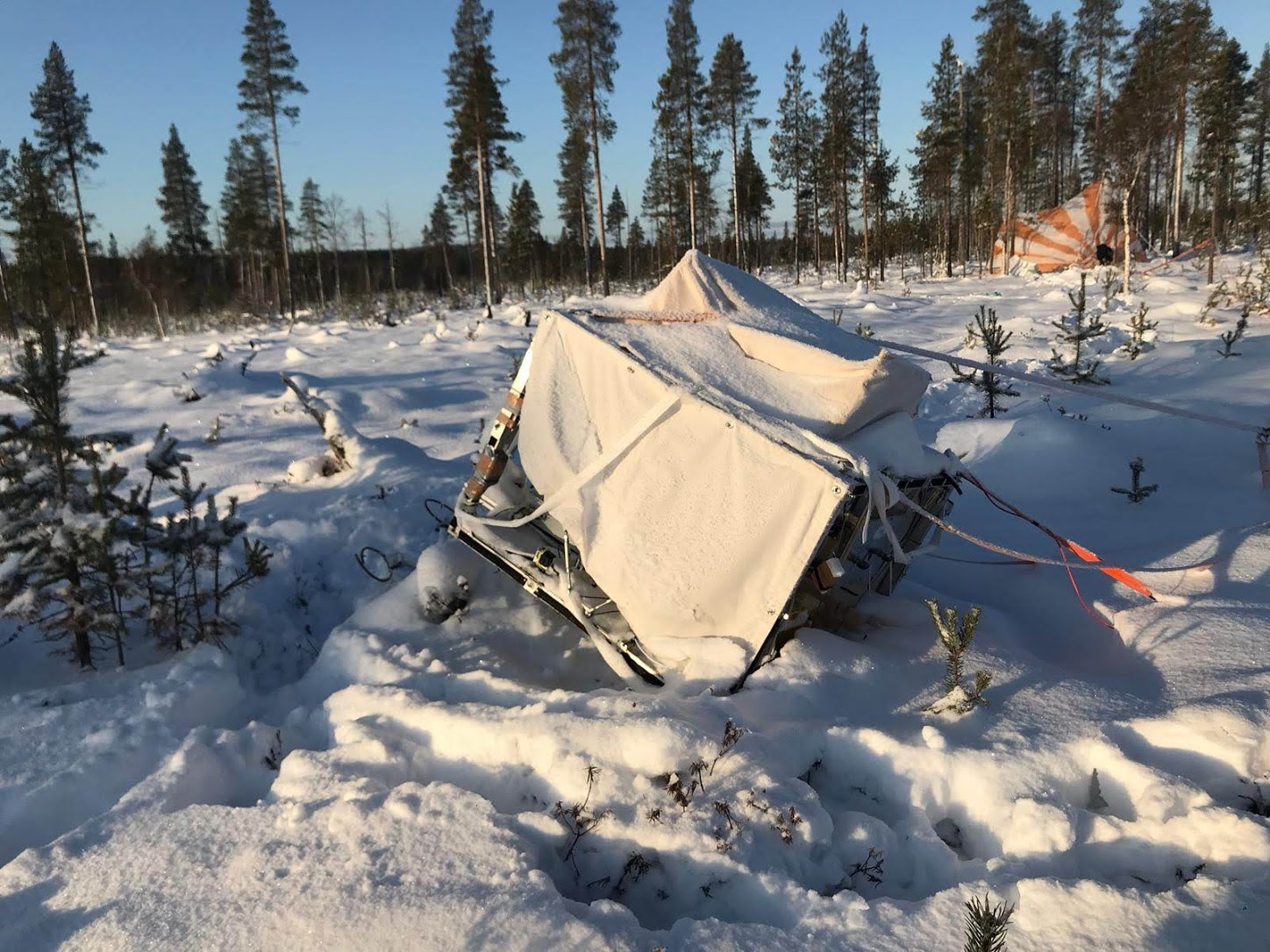
Purpose of the flight and payload description
BEXUS which stands for Balloon Experiments for University Students is a project part of the REXUS/BEXUs initiative that allows students from universities and higher education colleges across Europe and more recently also Canada to carry out scientific and technological experiments on stratospheric research balloons. The basic idea behind BEXUS is to provide an experimental space platform for students in different areas of interest such as atmospheric research, fluid physics, magnetic field, materials science, radiations physics, astrophysics, biology and also to serve as a platform for new technology demonstrations.
Each year, two balloons are launched from the European Space Range (ESRANGE) base near Kiruna, Sweden each carrying several experiments assembled on a medium-sized gondola (1.16 m x 1.16 m x 0.84 m). The total lifted-mass is approximately 300kg on each flight. With each payload weighing between 30 and 112 kg that means that 4 student experiments can be accomodated per gondola.
The first five flights of the program were carried out under sponsorship of the Swedish Space Corporation that offered available space on yearly technological flights carried out at ESRANGE. Since 2008, BEXUS is realised under a bilateral Agency Agreement between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the Swedish National Space Agency (SNSA). The Swedish share of the payload is made available to students from other European countries through a collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA). EuroLaunch, a cooperation between ESRANGE and the Mobile Rocket Base (MORABA) of DLR, is the organism responsible for the campaign management and operations of the launch vehicles.
On each cycle of the initiative, experts from DLR, SSC, ZARM (Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity, University of Bremen) and ESA provide technical support to the student teams throughout the project. It begins with a Call for Proposals, followed by a condensed space project lifecycle, including typical design phases and reviews, culminating in the launch of the experiments and publication of the final reports.
Details of the balloon flight
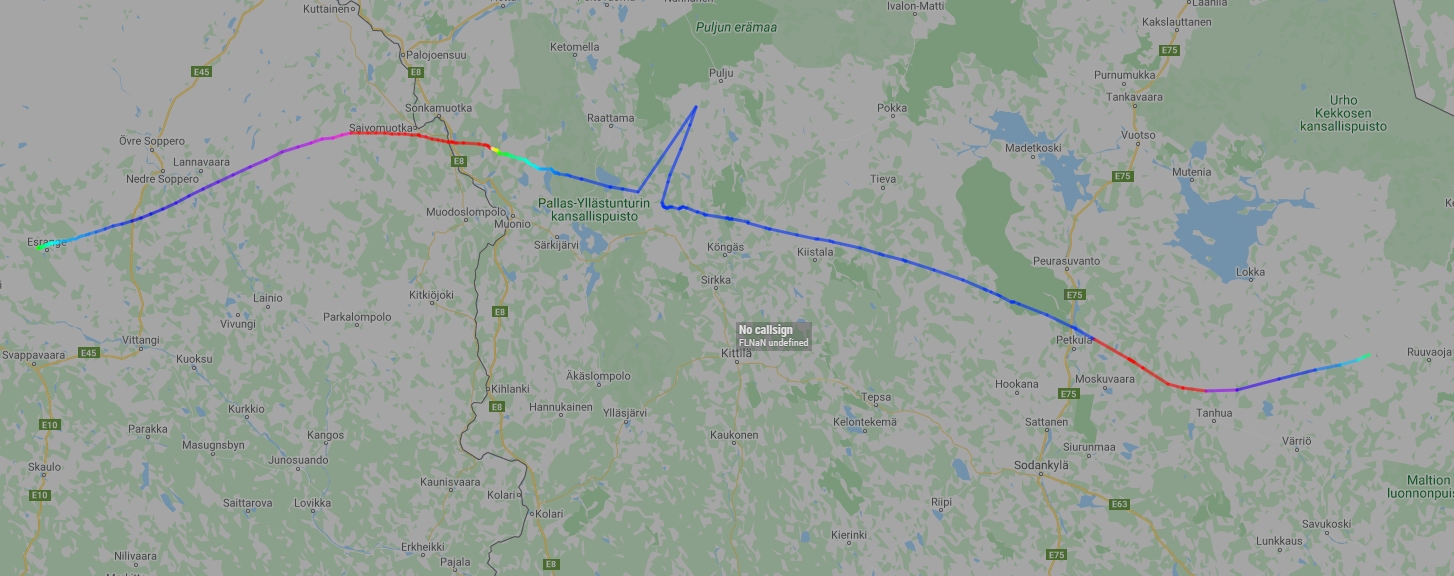
Balloon launched on: 10/25/2019 at 4:21 utc
Launch site: European Space Range, Kiruna, Sweden
Balloon launched by: Swedish Space Corporation (SSC)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon model 35SF Airstar 35SF - 35.000 m3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 10/25/2019 at
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 3 h 30 m
Landing site: W of Ruuvaoja, Finland
Campaign: BEXUS
Payload weight:
Gondola weight:
The experiments that were part of Bexus 28 flight were:
OOXYGEN stands for Organic Oxygen sensor reference experiment. Developed by Technische Universität Dresden, Germany is aimed to test a novel optical oxygen sensor which is based on biluminescence.
TARDIS acronym for Tracking and attitude radio-based determination in stratosphere. A development by University of Rome, La Sapienza to test an alternative in-flight attitude and position determination system based on the processing of the VOR signal and a radio-based tracking system.
IRISC stands for Infrared imaging of astronomical targets with a stabilized camera. It is an experiment developed by Luleå University of Technology, Sweden whose goal is to obtain images in the near infrared spectrum from astronomical targets including the Andromeda Galaxy, Pinwheel Galaxy, Iris Nebula, Eagle Nebula and Starfish Cluster.
GAMMA VOLANTIS also developed by Technische Universität Dresden, from Germany is a test bed for ozone and relative humidity sensors under real conditions.
DESTINY which stands for Detection of earthquakes through a stratospheric Infrasound study, is a development by the École Polytechnique, from France aimed to characterize the infrasonic background of the atmosphere to be able to recognize specific signals and locate their origin.
External references
- BEXUS website
- Gamma-Volantis website Star-Dresden
- IRISC experiment facebook page
- OOXYGEN website Star-Dresden
- Tardis Experiment facebook page
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.






