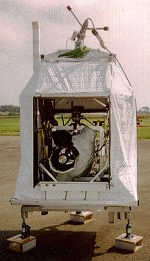
Purpose of the flight and payload description
AMON is a balloon-borne UV-Visible spectrometer aimed to obtain vertical profiles of O3, NO2, NO3, OClO and of the extinction coefficient of aerosols for altitudes ranging from 15 to 40 km. It is composed of a 20-cm Cassegrain telescope with a 1-meter focal length, a grating spectrometer, and a CCD detector. The instrument is mounted in a stabilized gondola developed by the Geneva Observatory.
AMON observations are performed by the stellar occultation method, which consists in analyzing, during the setting of a star, recorded spectra that are affected by atmospheric absorption by the species that are present in the lines of sight of the star. At a balloon float altitude of 3439 km, depending on the flight conditions, first a reference spectrum is recorded when the star is a few degrees above the horizon of the gondola in which the instrument is riding. Raw spectra are then recorded while the star is setting under the gondolas horizon. Transmission spectra are obtained by division of the stars occultation spectra by the reference spectrum. The spectrometer covers, continuously, the ultravioletvisible spectral domains in five spectral bands. The vertical resolution of this instrument is ~0.5 km.
The first technological flight of AMON was carried out in 1991, since then until 1998, AMON was the only balloon-borne instrument making measurements at night in this spectral range and thus the only instrument measuring NO3 from the stratosphere. From AMON measurements, it was shown the possibility of the presence of OBrO species as was predicted by models. Nowadays these measurements are taken regularly by the SALOMON instrument developed by the same laboratory.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 5/24/1992 at 1:00 utc
Launch site: Centre de Lancement de Ballons CLBA, Aire Sur L'Adour, Landes, France
Balloon launched by: Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 5/24/1992
This was the first technological flight of the instrument
External references
- The AMON Instrument: Absorption by the Minor components Ozone and Nox Atmospheric Chemistry Data Centre
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.