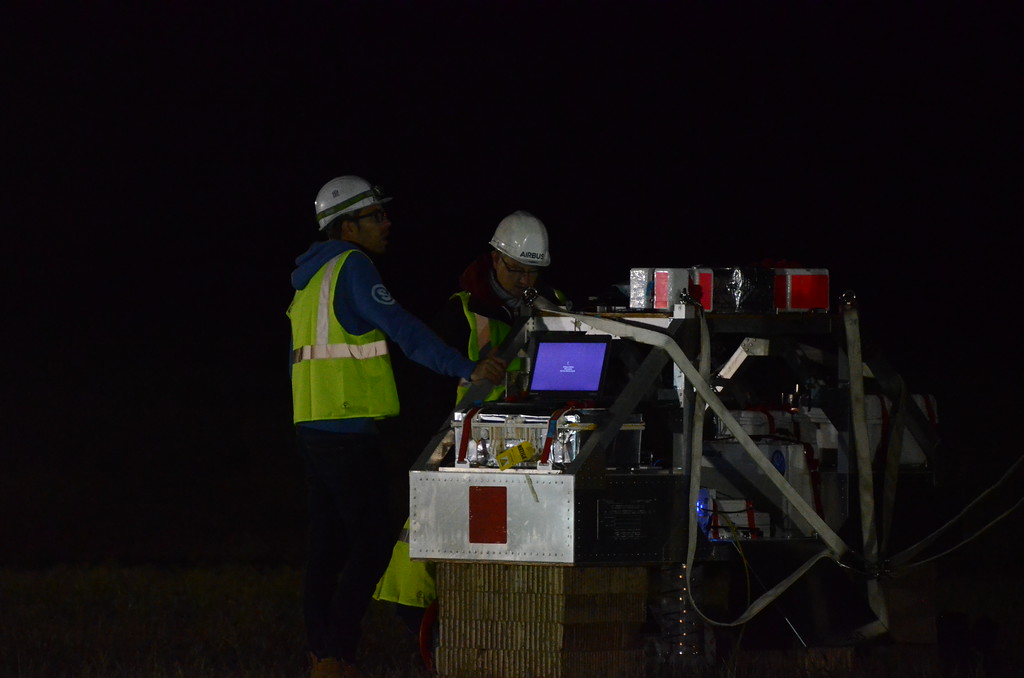
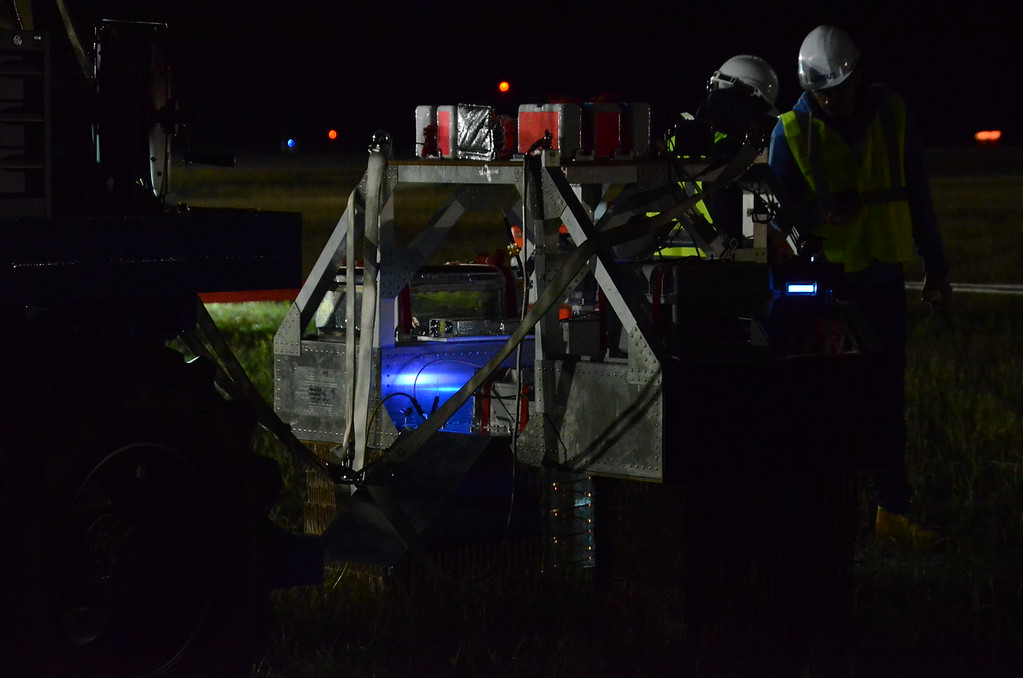
Purpose of the flight and payload description
The objective of the flight was to test a system developed by Airbus, a leader European firm in the field of aeronautics, space and related services, for stratospheric 4G/5G defence applications.
The technology tested on this balloon mission, an Airbus LTE AirNode, is a key part of Airbus' secure networked airborne military communications project, known as Network for the Sky (NFTS) which the company unveiled at the Farnborough International Airshow in July 2018. This long-range communication system would allow high-altitude platforms such as Airbus Zephyr to create persistent, secured communication cells to relay information on a variety of different aircraft platforms including helicopters, tactical UAVs and MALE UAVs (Medium Altitude Long Endurance Unmanned Aerial Vehicles).
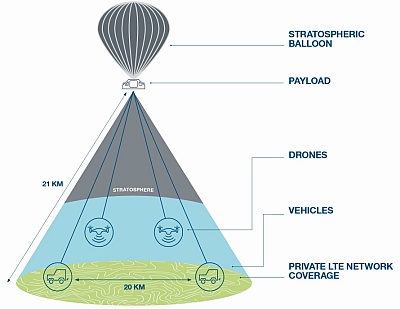
The Airbus LTE AirNode flown in the Nimbus-3 flight created below the balloon a so called "high-altitude airborne cell" a 30km-wide footprint of coverage for private and secure communications. At left we can see an scheme that explains the mission profile.
The Airbus team, equipped with two vehicles and two drones, tracked the balloon over 200 km, exchanging 4K video between the different platforms, simulating an ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance) mission with real-time transmission. The data was sent via a private network at speeds from 0.5 to 4 Mbps, which is comparable to 4G/5G mobile communication.
Several additional Canadian experiments were also included in the gondola:
Otachi Probe and ProtosAT a probe and a CubeSat prototype developed by NaniKana Aerospace, a non-for-profit organization from the Abitibi-Temiscamingue region. During the flight was tested the radio communication modules, the power module and was also filmed the ascent of the CubeSat.
SEDS CAN-SBX Challenge AlbertaSat Team Payload MIIST The AlbertaSat team, from the University of Alberta, is one of the teams selected by SEDS as part of a pan-Canadian competition to design, build and fly their experiments. SEDS is an organization that aims to provide students with research and development opportunities. With their payload MIIST, AlbertaSat team validated in flight the mechanical and electrical systems of their CubeSat and tested a multispectral imager, a tool that captures specific wavelength ranges in an image.
Power Distribution Unit and Battery developed by Canadian Space Agency with the collaboration of DPL Science Ltd. This modular subsystem consisted of a set of Li-ion batteries and a power distribution unit. It was developed to support payloads power requirements during STRATOS flights. Known as the STRATOS Power subsystem, this equipment provided power to the MIIST payload during the flight.
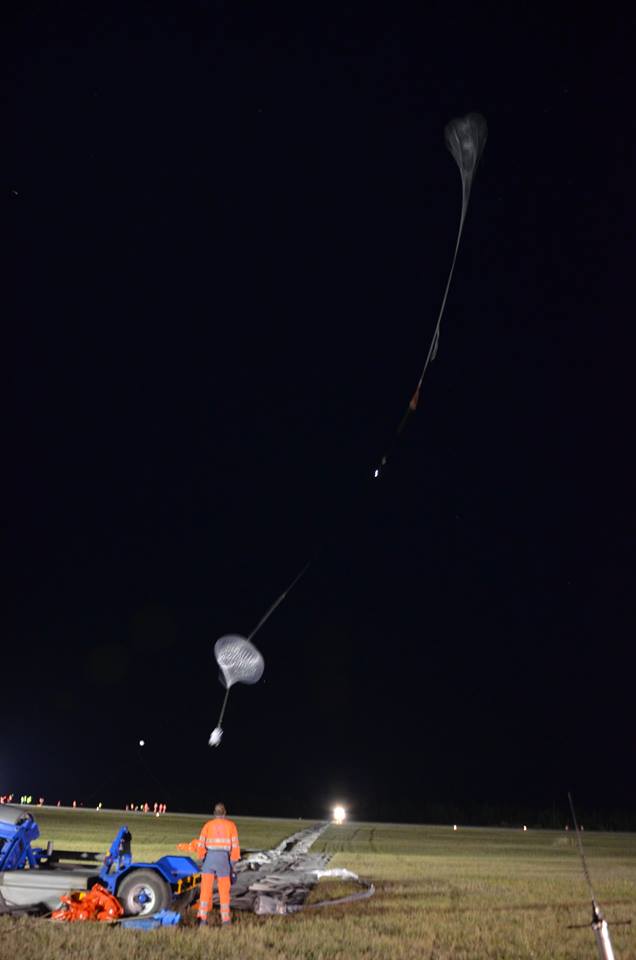
Video of the launch and ascent of the balloon and recovery of the payload
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 8/19/2018 at 4:30 utc
Launch site: Timmins Stratospheric Balloon Base, Ontario, Canada
Balloon launched by: Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon model 100z Airstar - 100.000 m3
Balloon serial number:
Flight identification number: NIMBUS-3
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 8/19/2018
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 11 h
Landing site: 40 km NW of Timmins, Ontario, Canada
Campaign: STRATOSCIENCE 2018
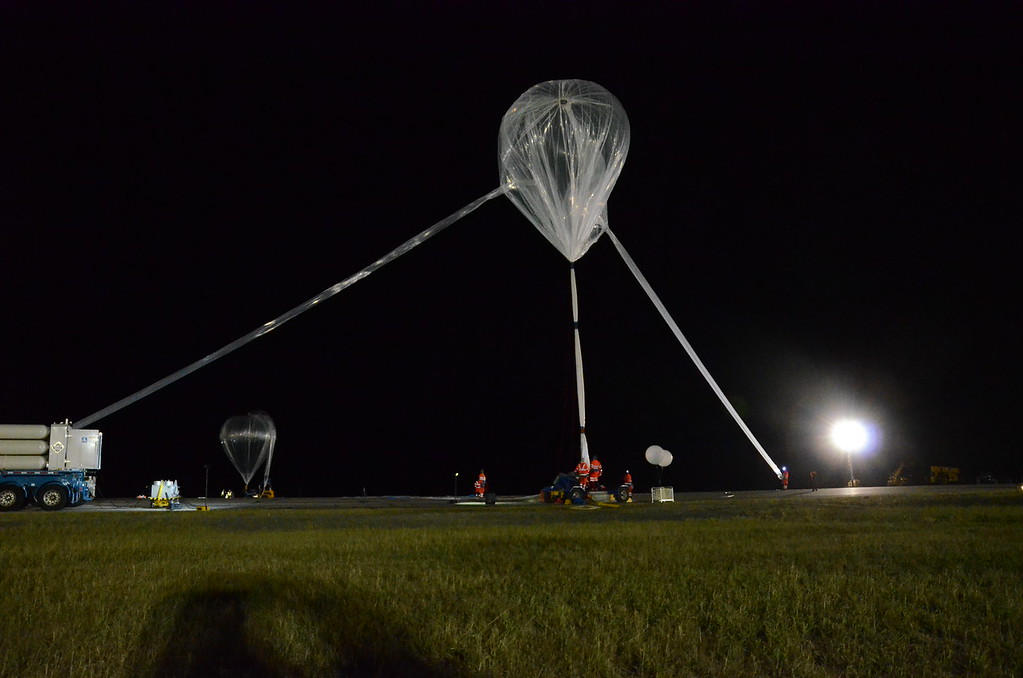
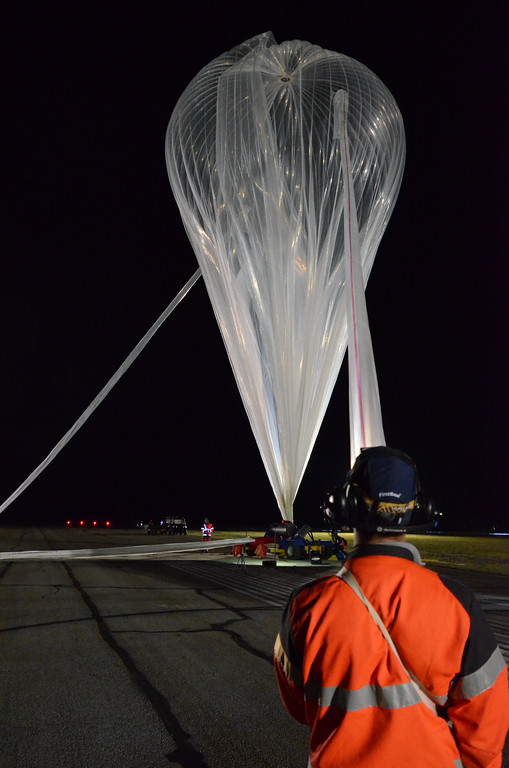
The balloon was launched as mission Nimbus-3 at 1:30 am on August 19, 2018 from the Timmins Stratospheric Balloon Base in Ontario, using the auxiliary balloon method. After a nominal ascent phase the balloon reached float altitude of 21 km which was maintained troughout the entire flight.
Once the mission was completed about 15:30 utc the termination command was sent and the payload was separated from the balloon. The gondola landed safely 40 km NW of Timmins Stratospheric balloon launch base. Total flight time was about 11 hours.
External references
- Network for the Sky: Airbus successfully tests stratospheric 4G/5G defence communications with balloon demonstration AIRBUS press release
- Pictures of the AIRBUS flight Timmins Stratospheric Balloon Base album at SmugMug website
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.