Purpose of the flight and payload description
This flight was devoted to test a new detector called TINMAN acronym for ThermalIzed Neutron MeAsuremeNt experiment which was developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory in collaboration with Honeywell, Inc. Aerospace.
TINMAN was designed and built to address a recent concern in the air industry about thermal neutrons causing single event effects in semiconductor devices. Thermal neutrons are produced in an airplane when high energy-neutrons, created by the interaction of cosmic rays in the atmosphere, are thermalized in the fuel, the passengers and the airplane itself. Therefore, they are very environment dependent. Airplanes are a particular concern because at aircraft altitudes, the cosmic-ray neutron flux is approximately 300 times the sea-level neutron flux. Therefore, the understanding of the thermal neutron intensity at aircraft altitude is critical for understanding the risks of thermal neutrons to avionics systems.
The TINMAN detector consists of two 3 He ionization chambers. One of the 3 He ionization chamber is wrapped in a thin layer of cadmium. Because the cadmium shielding attenuates the thermal neutrons, the difference in count rates between these two detectors reflects the number of thermal neutrons detected.
Details of the balloon flight
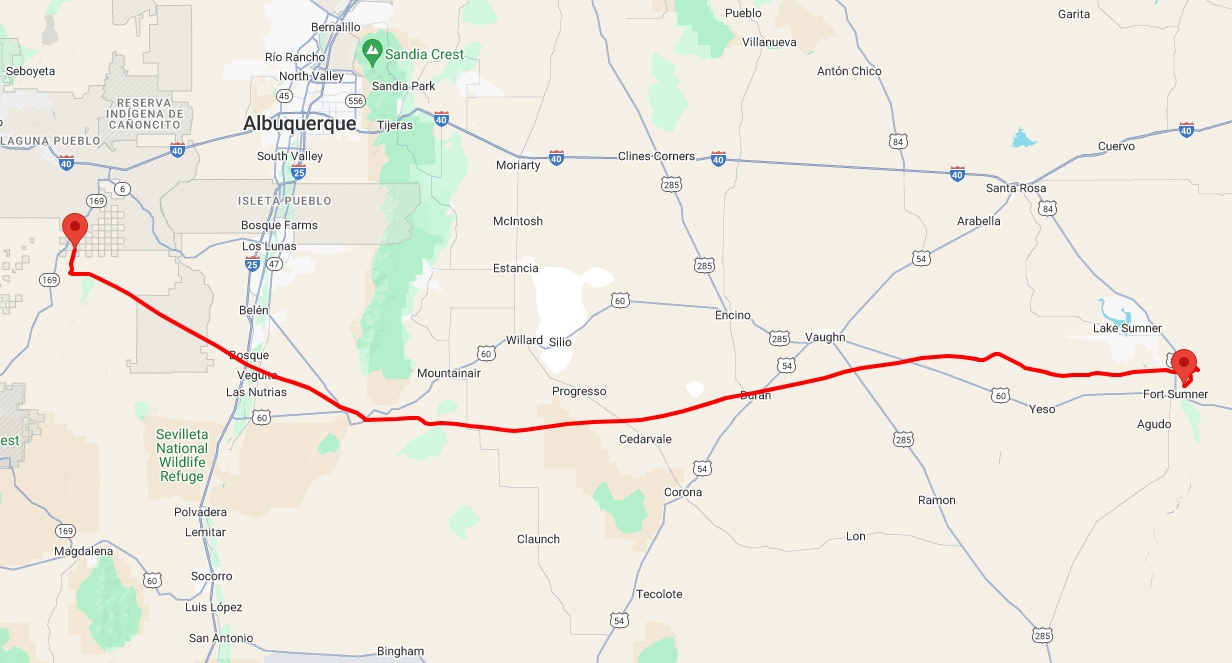
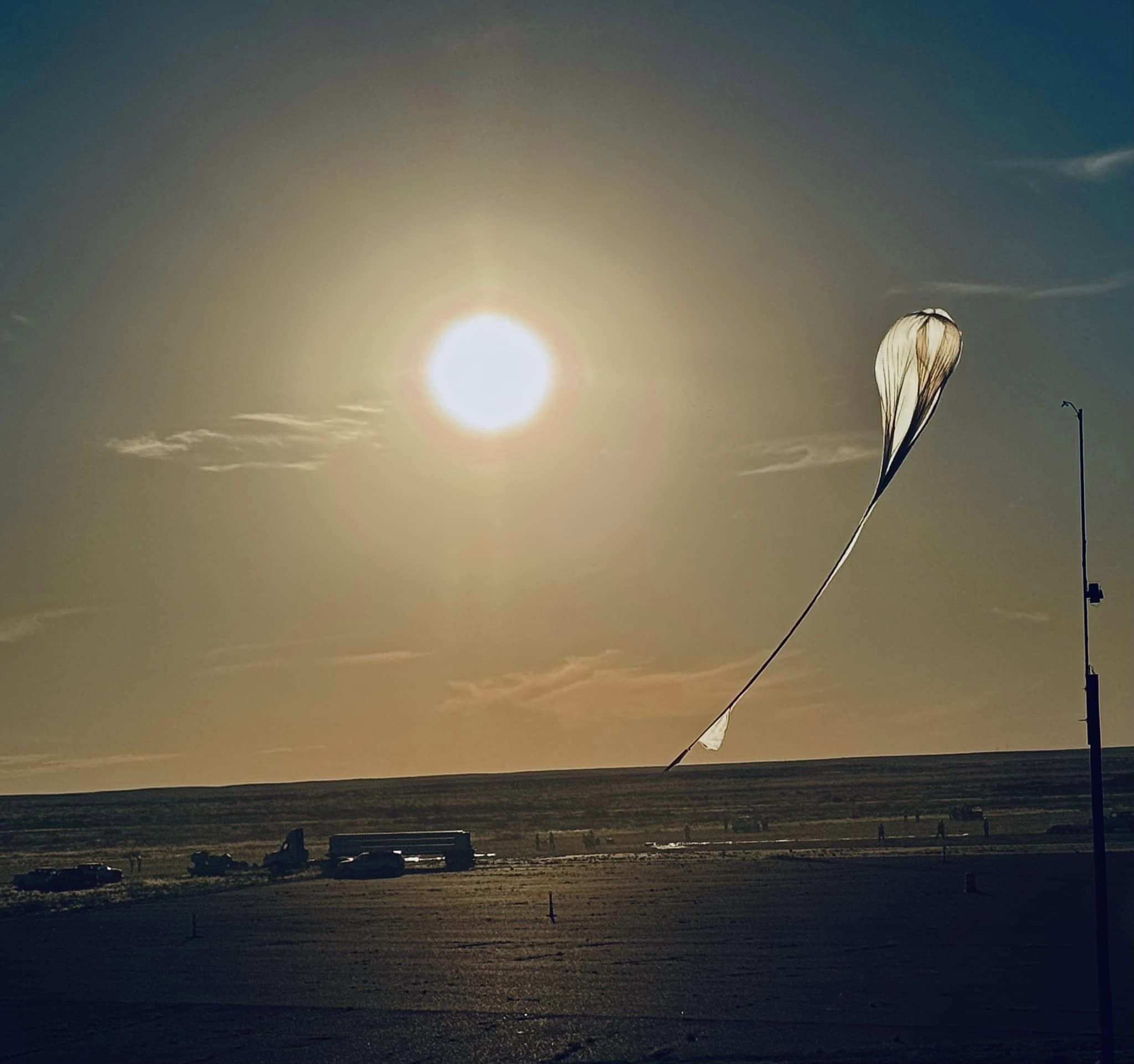
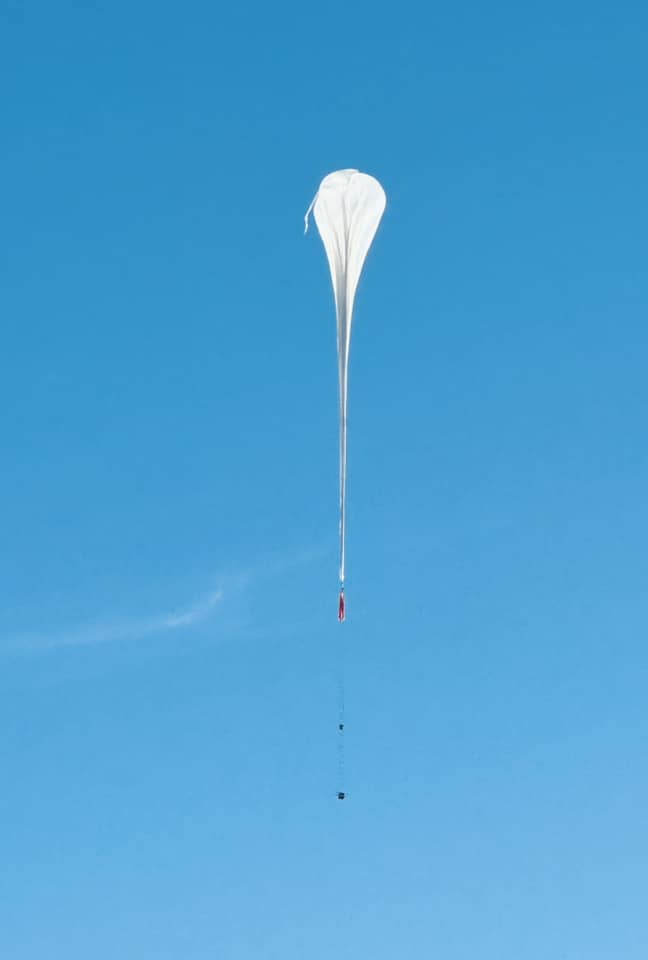
Balloon launched on: 8/21/2024 at 13:08 UTC
Launch site: Scientific Flight Balloon Facility, Fort Sumner, (NM), US
Balloon launched by: Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility (CSBF)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon
Flight identification number: 742N
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 8/21/2024 at 19:18 UTC
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 6 h 10 m
Landing site: 45 km W of Los Lunas, New Mexico, US
External references
- NASA to Launch 8 Scientific Balloons From New Mexico NASA website
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.



