Purpose of the flight and payload description
This test series was the first in a program of three test series designed to develop a new parachute system for Mars exploration as starting the new century, many of the lander missions under consideration included payloads that were five times more massive than those of previous missions. The program was carried out by the the Jet Propulsion laboratory, California Institute of Technology and Pioneer Aerospace with the support of NASA's National Scientific Balloon Facility.
The approach adopted instead of developing and qualifying a new system for these missions was to perform balloon-based drop tests of a 33.5 m Ringsail Canopy subsonic parachute to be used in conjunction with the existing supersonic Viking parachute as part of a two-stage system. The reason to use stratospheric balloons to tests this new design is based in the fact that in general, the atmospheric density near Mars surface is equivalent to Earth densities at altitudes between 30 and 35 km. The gondola plus canopy mass flown in these tests were 980 kg which corresponds to a Mars system mass of about 2500 kg.
At left we can see an image of the gondola used for the tests (click for more details). It was a simple truss structure that included a faceted aerodynamic fairing to produce an aerodynamic wake similar to that expected from a hypersonic entry capsule of diameter of about 3.5 meters. The fairing assured the parachute inflated and operated in wake conditions similar to those expected on Mars. The structural base of the gondola was a 2.54 cm thick steel regular nonagon (a nine sided polygon with equal sides) with paper honeycomb crush pads mounted for ground impact energy absorption. On top of this base plate the batteries, instrumentation, pyrotechnics, and balloon telecommunications equipment were mounted. Bipod trusses connected the base plate to three structural nodes at the parachute deck above. Both the drogue triple risers and the main triple risers were attached to these structural nodes. The main ringsail canopy was stowed in an annular deployment bag on the parachute deck and the smaller drogue deployment bag was stored on top of the main. Staging of the main parachute was commanded by a pyrotechnics system on the Gondola. Cuting wires in the gondola released cutters activated timers in the on-board pyrotechnics system. When these timers expired, they commanded cutters at each structural node that simultaneously severed the three drogue triple risers.
The gondola carried four cameras: three up-looking cameras to observe the deployment and operation of the drogue and main canopies, one horizon looking camera, and one down-looking camera. The later was part of a separate experiment dedicated towards obtaining visual imagery for optical navigation of a pin-point landing technology task. Additional imagery was collected via a ground-based telescope fitted with a video camera and another video camera in the chase airplane.
The instrumentation suite included numerous sensors to record the deployment, inflation, and inflated performance of the parachute. All data was stored by an on-board, low power CPU with flash memory storage. The memory capacity (and Lithium-ion battery power supply) was sized for a 10 hour duration. This time accounted for potential delays in launch, or extended period at float while an acceptable descent corridor was found.
A Northrop Grumman LN-200 Inertial Measurement Unit included 3-axis accelerometers and 3-axis rate gyros for obtaining detailed data on gondola dynamics. Load cells were mounted in-line on each of the main parachute triple risers. In addition to providing a direct measurement of inflation loads, the load cells could describe the motion of the parachute relative to the gondola. A Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver and antennae were included to provide rough trajectory and altitude information. Five pressure transducers and numerous temperature transducers were also included.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 9/11/2004 at 14:23 utc
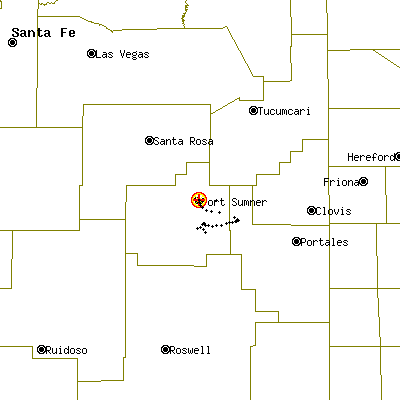
Launch site: Scientific Flight Balloon Facility, Fort Sumner, (NM), US
Balloon launched by: National Scientific Balloon Facility (NSBF)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon Winzen - 11.820.000 cuft (0.8 mil) - SF3-11.82-.8/.8-NA
Balloon serial number: W11.82-1E-30
Flight identification number: 531N
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 9/11/2004 at 16:27 utc
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 2 h 17 min
Landing site: 15 miles S of Ft.Sumner, New Mexico, US
Payload weight: 2175 lbs
Overall weight: 2529 lbs
This was the second test in the series. The balloon was launched from the Scientific Flight Facility in Fort Sumner, New Mexico at 14:23 utc on September 11, 2004. Launch preparations, launch, and ascent went as expected.
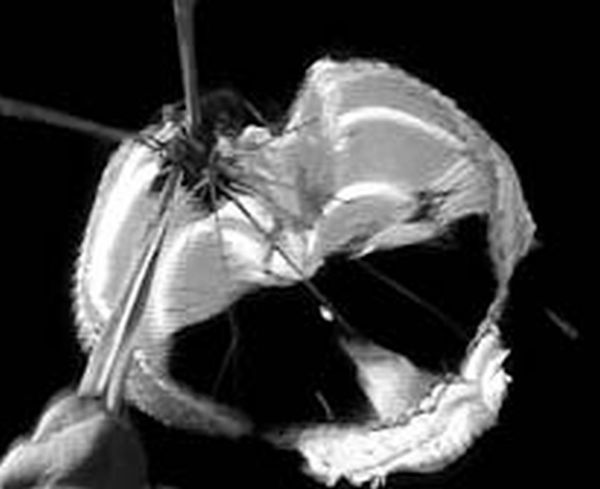
The payload was released from 36.3 km. Drogue deployment was significantly improved from test 1. Main deployment occurred at the correct conditions, however, canopy entanglement and improper reefed state again resulted. At disreef, the canopy suffered substantial structural failure as can be seen in the image at right. Review of the telescope video revealed another apex rebound during deployment indicating inadequate vent control. Inspection of the recovered pieces revealed that the redesigned vent control leash deployed and performed as designed, but the strength was inadequate. The apex rebound drove the vent region of the canopy into the lower inflating portion of the canopy at speeds around 40 m/s. This produced another entanglement and led to the ensuing canopy damage. The significantly reduced drag area of the parachute provided some deceleration to the payload. It touched ground at 16:40 utc 15 nm south of Fort Sumner, NM at coordinates 34º 14.6 North / 104º 10.4 West. Ground impact was estimated at 18 m/s. The crush pad provided significant impact energy absorption, but the gondola suffered some structural deformation and several electrical cables were damaged.
Additional investigation into the Vent Control Leash design was undertaken and revealed that the redesign from test 1 solved the stowage and deployment problems experienced there, but instead revealed that the strength was inadequate for the high altitude conditions. Inadequate strength decreased the time which the leash controlled the vent and allowed the vent to attain significant out-of-column attitudes. The strength and length of the vent control leash were increased.
External references
- High Altitude Test Program for A Mars Subsonic Parachute 18th AIAA Aerodynamic Decelerator Systems Technology Conference and Seminar
- Inside Wallops Volume XX-04 Nº 31
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.