Purpose of the flight and payload description
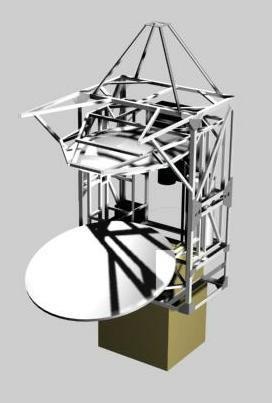
The Background Emission Anisotropy Scanning Telescope (BEAST) is a millimeter wavelength experiment designed to generate maps of fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The primary reflector (the largest flown on a stabilized balloon platform) is a 2.2 m off-axis parabolic reflector that receives its input beam from a rotating flat reflector of 2.6 m in diameter. The telescope focuses the collected microwave radiation onto an array of cryogenically cooled high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) receivers. This array is composed of six corrugated scalar feed horns in the Q band (38 to 45 GHz) and two more in the Ka band (26 to 36 GHz) with one of the six Q-band horns connected to an ortho-mode transducer for extraction of both polarizations incident on the single feed.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 5/20/2000 at 14:23 utc
Launch site: Scientific Flight Balloon Facility, Fort Sumner, (NM), US
Balloon launched by: National Scientific Balloon Facility (NSBF)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 800.000 m3 - SF3-29.47-.8/.8/.8-NA
Balloon serial number: W29.47-2X-51
Flight identification number: 482N
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 5/21/2000 at 11:21 utc
Landing site: 5 miles E of Sunray, Texas, US
This was the first flight of the instrument. No useful data was obtained due to the fact that the reflecting
surface of BEAST's rotating flat reflector delaminated from its honeycomb core during balloon ascent.
External references
- A Map of the Cosmic Microwave Background from the BEAST Experiment The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Volume 158, Issue 1, pp. 101
- Imaging the cosmic microwave background: The BEAST experiment AIP Conferences. Proceedings. 555, 324 (2001)
- The Background Emission Anisotropy Scanning Telescope (BEAST) Instrument Description and Performances The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Volume 158, Issue 1, pp. 124-138
- The Optical Design of the Background Emission Anisotropy Scanning Telescope (BEAST) The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Volume 158, Issue 1, pp. 118
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.