Purpose of the flight and payload description
The payload on this flight was a gamma ray spark chamber experiment developed by the Max-Planck-Institut für Physik und Astrophysik, from Germany to observe low gamma rays from astronomical sources.
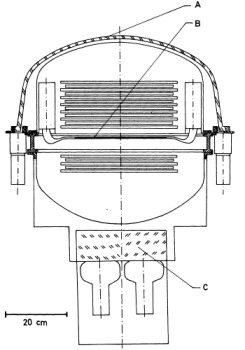
A schematic drawing of the instrument is shown at left. It consists of a wire spark chamber vessel sourrounded by an anticoincidence dome (A) which is triggered by a coincidence between thin (~ 2 mm) plastic scintillator counters (B) and Cerenkov counters (C). The scintillator (B) is embedded in the wire spark chamber.
That portion of the chamber situated above the scintillator (B) consisted of 13 plates (12 gaps) of 0.0114 cm thick tungsten with a repat separation of 12.4 mm, while the part situated below the scintillator (B) consisted of 4 gaps and did not contain any material apart from the wires. In this way, particle tracks can be recorded inside the volume of the telescope, but these particles are not absorbed or scattered in any material, apart from the 1.4 mm of the aluminum pressure vasel. This design feature increases the sensitivity of the instrument for low-energy gamma rays.
Each of the counters (B) and (C) was subdivided into 4 quadrants that could be operated as 4 independent parallel telescopes.
Each event recorded in the spark chamber was transmitted to the ground by a PCM-telemetry system. The data sent included the time of occurrence, which was obtained with an accuracy to within 0.1 msec by an on-board quartz-stabilized clock, as well housekeeping information. Once the data was received at the ground station, the time information was checked against the mark of the WWV time signal station, for double control.
The experiment was pointed by means of an equatorial mounting on the oriented gondola. The orientation was achieved by rotating the gondola against the balloon and by a flywheel stabilization based on magnetometer attitude measurements.
Details of the balloon flight
Balloon launched on: 6/15/1970 at 7:01 cdt
Launch site: Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility, Palestine, Texas, US
Balloon launched by: NCAR National Scientific Balloon Flight Station
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon Winzen 20.000.000 cuft (0.6 Mil. CAP. 1.0 Mil. Stratofilm)
Balloon serial number: Serial Nº 1
Flight identification number: 560P
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 6/15/1970
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): F 6 h 35 m
Landing site: Pecos, Texas, US
Payload weight: 1243 lbs.
This was the second flight of the instrument. It was launched on June 15, 1970 from Palestine, Texas and reached an altitude of 2.1 mb.
The objective of the mission was to observe the Crab pulsar using a gamma ray spark chamber experiment.
Two malfunctions occurred during this flight. First, the balloon rotated more violently than had been anticipated. Thus, the orientation system occasionally lost the Crab during periods of large angular velocity of the balloon, and the total observation time was thus reduced to 10876 seconds. Secondly, electromagnetic interference from the telecommand system occasionally caused sudden jumps to occur in the readings of the on-board clock. After the flight, the scientific team was able to eliminate these errors by a lengthy process of comparison of the on-board clock values with the signals from WWV recorded on ground.
A total amount of 815 events were selected for analysis, more or less a 23% of all spark chamber triggerings.
External references
- Investigation of Gamma Radiation from the Crab Pulsar 12th International Conference on Cosmic Rays, Tasmania, Australia, 16-25 August, 1971. Volume 1., p.57
- NCAR Scientific Balloon Facility Annual Report, 1970 National Center for Atmospheric Research, February 1971
- Observation of the Diffuse Cosmic Gamma Radiation in the 30-50 MeV Region Astrophysical Journal, vol. 175, p.L23
- Review of Recent Performance of Large Balloons and Balloons with Payloads in Excess of 3000 Pounds Proceedings, Seventh AFCRL Scientific Balloon Symposium, 1973
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.