Purpose of the flight and payload description
STRATCOM (STRATospheric COMposition) was a long-term, multi-purpose program for integrated, correlated measurements of stratospheric parameters related to composition, thermodynamics, and radiative balance. It was a joint undertaking of several laboratories whose combined scientific, engineering, and field capabilities made possible an extensive program of multiple related measurements in the very complex and variable stratosphere. The program was born in 1968 by the initiative of the US Army's Atmospheric Sciences Laboratory (ASL), under the direction of Harold N. Ballard. Starting from the third mission in 1972, the program progresively incorporated other research institutions. A total of eight balloon flights were performed until the culmination of the effort in 1977.
Details of the balloon flight
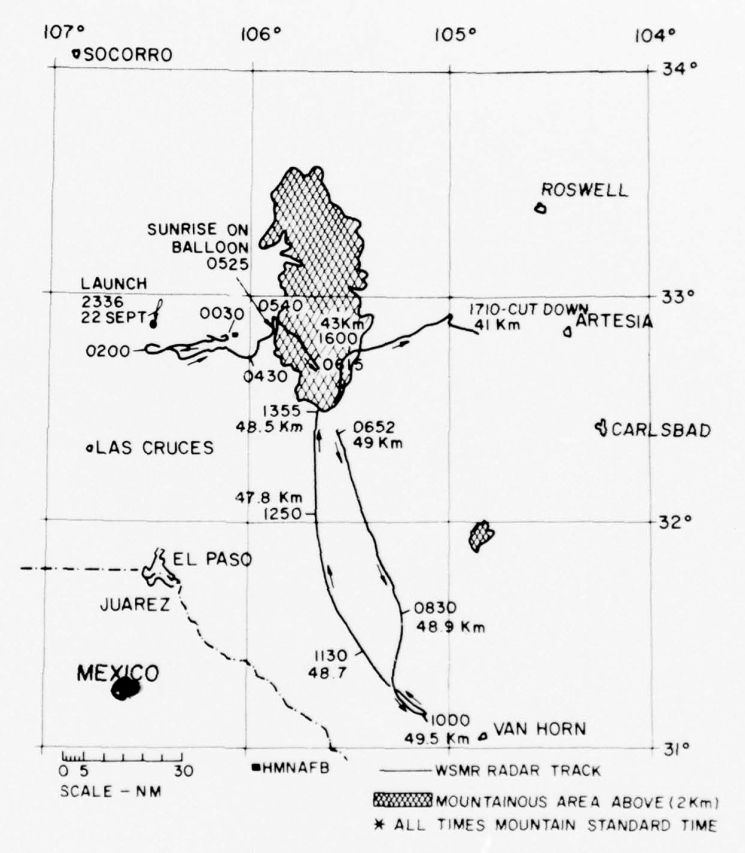
Balloon launched on: 9/22/1969 at 6:36 utc
Launch site: White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, US Pony Site
Balloon launched by: Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories (AFCRL)
Balloon manufacturer/size/composition: Zero Pressure Balloon 30.300.000 cuft
End of flight (L for landing time, W for last contact, otherwise termination time): 9/23/1969 at 00:10 utc
Balloon flight duration (F: time at float only, otherwise total flight time in d:days / h:hours or m:minutes - ): 18 h
Landing site: 25 miles W of Artesia, New Mexico, US
This was the second flight of the program. Their research goals were the same of the first flight performed from the same site in 1968 but with some improvements in the experiments. It transported instruments for the measurement of temperature, pressure, density, and related ozone and water vapor concentrations near 48 km and to study the atmospheric tides that rocket soundings have indicated exist in the atmospheric region from 40 to 60 km.
External references
- A balloon measurement of ozone near sunrise U.S. Army Electronics Command, White Sands Missile Range, 1969
- Atmospheric Tidal Measurements at 50 km from a Constant-Altitude Balloon J. Appl. Meteor., 11, 11381149
- Temperature Measurements in the Stratosphere from Balloon-Borne Instrument Platforms, 1968-1975. Research and Development technical rept., ARMY ELECTRONICS COMMAND FORT MONMOUTH
If you consider this website interesting or useful, you can help me to keep it up and running with a small donation to cover the operational costs. Just the equivalent of the price of a cup of coffee helps a lot.